The “Covid-19” pandemic emphasized the importance of public health in the comprehensive power equation of states, especially as it clearly revealed that countries with strong health systems are capable of dealing with emergency health crises and disasters. Public health can maintain the cohesion and internal stability of the state, which in turn is translated into weightiness and political influence in the international arena.
The concept of the comprehensive power of a state refers to the elements or criteria that represent public resources used to boost its power, such as geographical location, human power, economic resources, political and diplomatic weight, armed forces, and scientific and technological possibilities. This means that the comprehensive power of any state is the sum of what it possesses of these resources combined, and how they are employed effectively and efficiently to enhance its position on the international arena.
The concept of comprehensive power has witnessed fundamental transformations over the past decades. During the “Cold War” era, the focus was mainly on military force as the core of the comprehensive power of states. If any state to succeed in enhancing their national security, it must possess strong military forces and sufficient deterrent factors against its opponents. But, this perception was proven wrong and new theories emerged after the end of the Cold War, dealing with the comprehensive power of states from a comprehensive strategic point of view, that takes into account other aspects of power: economic, political, social and technological. This concept has developed in the past few years to add elements of soft power, as culture, media and human values to the concept of comprehensive power of states.
“Covid-19” and the shift in the comprehensive power concept
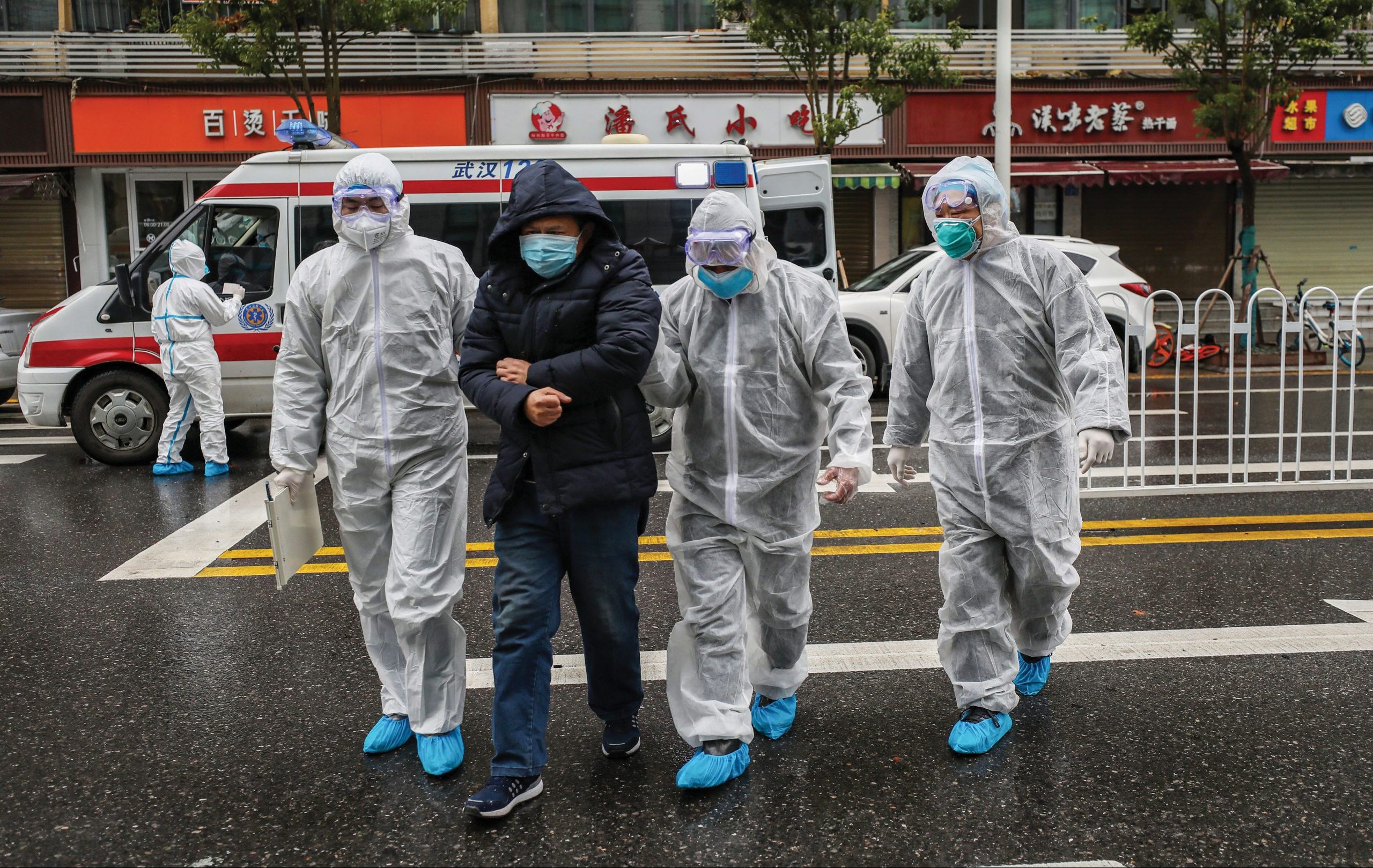

It is no exaggeration that the emergence of the Corona virus; “Covid-19” in the Chinese city of Wuhan in December 2019, and its transmission to the whole world, constituted, and continues to do, the most serious health crisis facing humanity in contemporary history. The outbreak of the virus raised many essential questions, related to the concept of the comprehensive power of states and the criteria for its evaluation, especially after this pandemic revealed the weakness of the health systems in many advanced industrial countries, showing their inability to provide health care to their citizens in the first months of the pandemic’s emergence. On the other hand, some countries, not classified developed, were able to deal with this pandemic effectively. They succeeded in providing an umbrella of advanced health care for their peoples, because of their ability to employ the health systems efficiently, either through increasing the number of tests, or by applying advanced systems to track the infected cases and enforce quarantine. As a result of this success, they were able to contain the virus and mitigate its various repercussions.
The serious repercussions of the “Covid-19” pandemic have prompted many countries to rearrange their priorities and evaluate their comprehensive power factors. They started to take health aspects into account; such as a strong health infrastructure of advanced hospitals, a strong medical sector, human resources, especially qualified doctors and nurses, as well as the availability of medical supplies, such as masks, respirators, etc. These preparations are considered now as the most important factors of comprehensive power. Moreover, the concept of “White Army”, in reference to the medical and health teams who are confronting this pandemic on the front lines, has become one of the main concepts providing evidence of how investing in the human aspect of the health sector is important.
The “Covid-19” pandemic has confirmed the importance of the public health for peoples, as the most important factors affecting the comprehensive power equation of states. The “Washington Post” published a significant article on the seventh of April 2020, in which the writer concluded that: “Because of this pandemic, the traditional assumptions about power that dominated the 20th and early 21st centuries could become undone. Instead, a new age of power may emerge in which far different state capacities, resources and priorities will be needed to compete on the world stage and meet the new set of international challenges…. modern governments should regulate and dominate their populations by vaccinating, treating, nourishing their peoples”.
According to the article, the United States still has the largest economy, the strongest army, and retains the world’s leading currency (the dollar), which is to say it leads the world in so-called hard power, but the coronavirus has already exposed that it lags far behind in terms of its demographic health. Public health system is unequal and severely underfunded, which imposes grave danger on US national security if these problems are not treated.
The impact of the pandemic
The “Covid-19” pandemic has enhanced the role of public health for the peoples. It has become among the most important criteria to measure the comprehensive power of states. That is reflected in the following aspects:
1 - Focus on Peoples’ “health security”: As it is one of the most important ingredients of the comprehensive power of the states, and the most important security pillar, clear strategies to develop the health systems are being adopted all over the world, especially after the massive destruction of the economic and human systems globally, as a result of the coronavirus. Many studies expect that Western countries, affected by the pandemic, will consider health security as a top priority on their agendas again. It will get the same level of attention paid to technology and defensive security, especially after the existing health systems in rich countries have proved their inability to deal immediately and effectively in containing pandemics similar to the coronavirus.
Many countries have already begun to pay exceptional attention to developing their health policies, whether through increasing investment in conducting scientific research to invent vaccines for various diseases, or by increasing the proportion of budgets allocated to the health sector in public budgets, or through developing and providing hospitals, as well as caring for medical sector; being at the core of the comprehensive national security of the states and communities.
At the same time, epidemics and viruses are seen now as one of the most dangerous threatening to the national security of the states.
In a clear reference to the danger of viruses and epidemics to societies and states security, the American “Foreign Affairs” Journal published an article in March 2020, titled: “Pandemic Disease Is a Threat to National Security Washington Should Treat It Like One”.
2 – New tasks for “Health Intelligence”: The “ “Covid-19” pandemic has prompted many countries to reconsider the tasks of the security and intelligence services, as a result to the new order the pandemic created. Talk is rising in a remarkable manner about the importance of establishing specialized “Health Intelligence”; to maintain the health security of states and their citizens, through examining health conditions, searching for biological threats, and analyzing all the information obtained, whether the source was digital media platforms, social media, or by using key words used on the internet, etc. They have to analyze the content of these information to get any indication of epidemic spread or any health crisis emerging anywhere. Then, they are to inform the concerned authorities, which in turn, take the necessary proactive measures to deal with the situation.
The escalating talk about the importance of having specialized “health intelligence” is due in part to the success of German intelligence in obtaining advance information about the coronavirus at the beginning of its spread in the Chinese city of Wuhan. It had reports talking about the spread of the epidemic in many Chinese cities, and obtained details about the virus and its symptoms, then informed the health institutions in Germany two weeks before announcing the spread of the virus. Consequently, German authorities moved quickly to take precautionary and preventive measures that have had the greatest impact in strengthening their capacity to cope with the pandemic, compared to many European countries, that have been affected significantly.
3 – Rehabilitation of the “White Army”: The name given to the medical teams of doctors and nurses who responded to the “Covid-19” pandemic, as the “White Army”, did not come out of nowhere. Rather, it was the result of the unprecedented efforts they made, and are still making, to counter this pandemic, that is considered as global challenge. They are on first lines like soldiers fighting on a battlefields, especially as they face an invisible and rapidly mutating virus, which caused growing global confusion.
The “Covid-19” pandemic has brought the “White Army” into account, and countries all over the world are competing to attract physicians and nurses, because they are the cornerstone of any sophisticated health system, in order to address cross-border epidemics and viruses. In March 2020, United States announced: “providing facilities regarding work and visit visas to its territories, for foreigners working in the health sector, as part of its efforts to confront the outbreak of the emerging coronavirus”. The US authorities singled out those who work in the field of combating the “Covid-19” pandemic.
At the same time, some German states called on immigrant doctors to return quickly, and “took the necessary measures to register them, in order to confront the pandemic”.
4 - Increasing demands for spending on global health: The “Covid-19” pandemic led to escalating demands to increase investments directed to the World Health Organization. The Director-General of the World Health Organization, Dr “Tedros Adhanom”, on the occasion of World Health Day in the seventh of April 2021, called countries all over the world to “invest in health as a motor of development. It is vital to invest in strengthening health services and to remove the barriers that prevent so many people from using them, so more people have the chance to live healthy lives”. He asserted the importance of “investing in primary healthcare, as more than half the world’s population still lack access to”. Adhanom called for bridging the global deficit of 18 million health workers needed to achieve the hedging of overall health by 2030, creating at least 10 million additional full-time job, and building safe, healthy, inclusive neighbourhoods”. He also called for “Strengthening data and information systems across the health sector by the significant vectors of age, race and ethnicity, sex, wealth, education, and place of residence”, to identify and address inequality. The increasing demands for spending on global health and investing in aspects of comprehensive health care is no longer a necessity only to combat the spread of viruses and epidemics, but it has its great developmental and social return as well, as it contributes to strengthening the comprehensive power of states, and helps them to deal with emergency health crises efficiently and effectively.
5 - Developing crises and health early warning systems: One of the repercussions of the “Covid-19” pandemic has been the increasing demands for the need to work on developing the system of health crises and disasters globally, to be able not only to deal with global health crises and pandemics that cross borders, but also to predict them in advance, and take proactive measures to confront them.
In fact, setting health early warning systems has become an urgent need, especially in light of expectations that the “Covid-19” pandemic will not be the last, and that the world may witness such crises or diseases in the future. This requires proactive measures from this very moment, by collecting information about any potential developing diseases and viruses, and presenting them in a timely manner to the relevant agencies and health authorities in order to take the necessary measures to confront them and limit their effect. The importance of health early warning systems lies mainly in the fact that they play a key role in the rapid assessment of epidemics, that is providing optimal response to public health threats, and alerting decision makers to take the necessary measures in a timely manner to prevent the spread of the epidemics and reduce their negative effect consequently.
Public health.. the most important criteria for assessing the comprehensive power of states
The prevailing trend in security and defense studies before the emergence of “Covid-19” at the end of 2019 was to underestimate the importance of public health in relation to the comprehensive power equation of states, as well as its impact on their foreign policy. This pandemic has clearly revealed that public health is not separated from comprehensive power of the state, but it is considered as most important factors serving the national interest of states at home and adding to their political weight internationally. Public health and its associated indicators have turned to be a standard key to calculate the comprehensive power of states, to the extent that some countries have made use of what is called “health diplomacy”, to enhance their political influence and international prestige, depending on successes they have achieved in dealing with the “Covid-19” pandemic. China comes first after offering itself as a model to follow; politically, economically and socially.
At the same time, the pandemic has led many countries to reconsider their health policies to keep pace with the world after “Covid-19”. Now, They include health aspects within the security and defense policies, in terms of recognizing that the strengthening comprehensive power requires taking into account working on military, economic, cultural, social, environmental and health tracks in parallel.
There has become an international growing trend to recognize the importance of developing the public health of peoples, being an investment in the comprehensive power of the state and national security protection. For example, the United States, under the administration of President, “ Joe Biden”, considered the development of the health system and to addressing the “Covid-19” pandemic as a top priority. This was demonstrated by the American “Interim Strategy Guidance”, issued in March 2021. It clearly confirmed that health pandemics are among the “greatest threats” facing the United States and the world in general. Indeed, the Biden administration revealed, in May 2021, an investment of 7.4 billion American dollars from the US bailout package to hire workers in the field of public health to combat “Covid -19” and prepare for public health future challenges.
In the same context, the United Kingdom abolished the British Public Health Authority, the body that the British were proud of as the main regulator of everything related to health aspects in the country, and established a new body, whose role is focused on health preventive aspects, and is intended to prevent any external health threats targeting the United Kingdom.
The “Covid-19” pandemic has shown the importance of public health in the comprehensive power equation for states. It also revealed investing in and improving the healthcare system may outweigh other aspects of power, in the long run. Public health, with its various indicators, represents a criterion for the power of the state and its ability to maximize benefit of different resources in enhancing its international status. The most clear evident is the competition for producing “Covid-19” vaccines. In part, the vaccine turned to be a competition between the major powers on influence and scientific and technological prestige. That’s way the Russian President “Vladimir Putin”, described, in May 2021, “Sputnik” vaccine saying: “It can be relied upon, such as Kalashnikov rifles”; a type of weapons dating back to the former Soviet Union era, and still used widely today.