Logistics is the main means that maintains the combat capability of the forces and makes them highly efficient and effective in the battlefield. There are many modern armies that have realized the importance of logistics in the battlefield, and that successful logistics will contribute to the success of the mission, and the opposite is also true, so many armies aim to focus on superiority in logistics to ensure victory on the battlefield.
The increasing and diversified development of the needs of modern armies requires efficiency in the logistics process to enable the military forces to achieve their desired national goals. It is also necessary follow the required methods to manage the logistics process. The ingenuity and strength of the forces these days require the comprehensive management of human, economic and moral forces. The rapid and continuous development of military equipment affects the armed forces and it has a profound influence on the logistics systems, as it affects the leaders’ approach to developing effective plans, as each country sets its strategic plans in accordance with its security, economic and political conditions, thus laying clear foundations upon which military principles are based. The state’s military policy is directly reflected in building, arming and developing the armed forces. The state also establishes its military principles in accordance with its strategic objectives and its geographical, human and economic capabilities.
Definitions and Concepts
Based on the previous philosophy, there are many definitions and concepts that describe logistics, and all of them point in one direction, the most important of which are the following:
Logistics is the integration of transportation, catering, warehousing and maintenance, realization of equipment, and contracting, and making it one work that ensures that no defect occurs in these areas, and paves the way for the completion of a specific mission or strategy.
Logistics is the science of planning, executing, moving and maintaining forces. It includes planning, development, ordering, storage, movement, distribution, maintenance, evacuation, and disposal of property.
After the two world wars ended and political and military stability took place in various parts of the globe, a frantic arms race exploded in many countries. The armies worked on restructuring their units, formulating their doctrines and military strategies, in a manner that suits future requirements, taking as their reference the lessons learned from the two world wars. Logistics received a large part of attention, and signs of modern and organized logistics appeared.
General Philosophy of Logistics
The general philosophy of logistics became as follows:
• Planning and implementation of logistics is carried out on three levels: strategic, operational, and tactical levels.
• Support levels are four levels: organizational, direct, general, and central.
• Each catering level requires support from the higher level, and support is provided to the lower level, and it is not permissible to exceed the next level and request support from the next level except in special cases.
• Short logistics lines give a strong distinction to military operations.
• Each support level has limited capabilities.
• Whenever the logistics chain is provided with high efficiency, this will have a positive impact on the readiness of the units and the morale of the soldiers.
• The logistics units must work in complete integration.
• The system of logistics depots and fixed maintenance workshops in the forces’ sites (camps) is relied upon.
• Each unit must maintain sufficient quantities of supplies for a specific number of days, to be able to carry out its combat missions until the arrival of a higher-level support.
• Each unit must rely on its means of transportation, and when needed, support is requested from the higher level.
• Organizational support – the lowest level of support – is provided to a battalion, direct support is provided to the level of a brigade, and general support is higher than the level of a brigade.
• Each combat battalion contains logistics platoons and provisions’ staff. Each brigade contains a logistics battalion, provisions’ staff, an engineering company and a medical unit to support it.
• Each unit owns an organizational and equipment schedule, which specifies the unit’s allocation of food supplies, and it must be adhered to.
• Effective support is the support that is done at the right time and place, and in the right quantities.
• The modern rationing policy focuses on effective logistics at a lower cost.
• Combat support service units provide support in the field, and they must be flexible in a way that helps them move behind the forces, and fast-moving elements emanate from them to provide direct support within the axes of progress.
• Making the most of autonomous systems in facilitating logistics and logistics procedures, and linking logistics units and warehouses to each other. Control of inventory and facilitation of ordering and dispense operations.

The importance of logistics
It is clear from the above the importance of logistics operations in the results of the battle, they contribute to winning victory or defeat. War does not break out just to improve tactics or to show the intelligence of the state, but happens to expand or protect the state’s resources, and these resources are either men, money, or stances and principles.
Tactics are plans, logistics are means, and both are methods of warfare. So, logistics cannot win the war, but its absence or insufficiency can cause defeat.
Logistics & its impact on strategy
Strategy is the comprehensive orientation of the armed forces to achieve the general goals or objectives of the state in the long run. It is also defined as: the art of mobilizing and directing the nation’s resources, including the armed forces, to support and protect its interests from its actual or potential enemies. Liddell Hart defined it as (the art of distributing and using various military means to achieve policy objectives).
And logistics is defined as: the process of planning, implementing, and securing the armed forces in the main bases and in the theater of operations with all material needs in the specified place and time. Storage warehouses, and a close relationship is formed between logistics and strategy as a result of the fact that the state’s economic position represents a large and important part of the general strategy, and economic factors have a direct impact on strategic goals, and thus there is a great overlap between logistics, national economy and strategy, so the strategy deals with defining objectives, procedures and ways that enable achieving them. Logistics aims to equip the armed forces, and provide them with material needs of transportation, maintenance and continuous medical care, and this can only be achieved with a strong economy.
Logistics tasks in the armies
1- Catering. It is allocated according to the volume of the human unit.
2- Clothes, individual equipment, tools, personal equipment…etc. It is also disbursed according to unit size.
3- Fuel (all kinds of fuels – greases – oils – diesel) and it is allocated according to consumption rates, distance, type of mission and environment.
4- Construction materials (timber – iron – scaffolding) and it is allotted according to special orders.
5- Ammunition (bombs, mines, missiles, ordinary bullets) and it is dispensed according to the type of mission, the type of weapons, and specific consumption rates.
6- Personal needs (soap, shaving tools, towels, toothpaste) are disbursed according to the size of the unit.
7- The main materials (tanks, cannons, vehicles, generators) are distributed according to the units’ systems and equipment schedules or according to special orders.
8- Medical materials They are dispensed based on mission type, environment, troop size, and other medical estimates.
9- Spare parts (other than medical spare parts supplies) are allotted according to scheduled loads of spare parts and storage lists prepared by each unit or according to the mission and situation.
10- The requirements for supporting non-military programs (agricultural equipment, agricultural grains, fertilizers, drilling machines).
Types of management planning
Logistics commanders must be familiar with the forms of management planning and the factors affecting it and its suitability for development and change when necessary, then they will be able to work efficiently and at any level of command (strategic, operational, administrative).Since planning procedures are characterized by multiple methods, divisions have been established to clarify the relationship between the types of planning and the interactions that occur between them, the most important of which is (planning of demands and capabilities), and this planning is the first step in the basic logistical work related to providing the material means necessary to implement the strategic plan, after that comes (planning of administrative aid), which represents administrative affairs in every sense of the word, and it includes details of logistics, transportation, storage, repair and medical insurance, and through it the size of military formations is determined, so are the number of equipment, mechanisms, warplanes of all kinds, naval units, weight of material tools, storage capacity, and the size of transportation means.
Obstacles to Successful Logistics
The development and multiplicity of types and forms of military equipment requires a trained and qualified administrative apparatus capable of providing logistics to a modern army in constant need of huge quantities of all kinds of materiel on an ongoing basis, and this entails a significant increase in the volume of financial allocations to cover these requirements, and this may cause the logistics some problems, the most important reasons for this are the following:
Planning Failure: The failure of administrative leaders to develop successful planning or the failure in any aspect of planning is one of the most important causes of administrative inflation. When there is a failure in planning for any military operation, it results in problems in administrative affairs that have a great impact on the conduct of military operations.
Lack of competence: There is a prevailing culture among some military commanders that tends to assign individuals with limited experience to work in administrative units and the failure to develop effective and advanced training programs that raise the efficiency of the military performance in the administrative apparatus, which makes these units unable to carry out their tasks as required, and this leads to the low level of administrative planning, and forcing those responsible for logistics to request additional numbers of individuals to cover the deficit resulting from the low level of performance, in addition to that the failure of administrative commanders to develop successful planning. In addition to that, deficiency in any aspect of planning is one of the most serious causes of administrative inflation,
Lack of discipline: Administrative discipline is not considered an independent topic from the discipline that is supposed to characterize all military personnel at all levels. What is meant here is the discipline of administrative aspects by administrative commanders and their subordinates in peace and war. The lack of these basic features in the administrative apparatus leads to the collapse of all elements of planning, organization and control, and spread of corruption in all its forms, including negligence, embezzlement, bribery and nepotism; evidence from the military history on that is abundant.
Impact of future wars on the flow of logistics
The soldier is considered the decisive tool for the battle, because he is the basis for dealing with weapons and equipment, regardless of progress and development. Therefore, the focus was placed on making the soldier self-reliant for a long period in the battle without the need for supplies or equipment, as a tremendous development took place, which made him an integrated unit by providing him with equipment, clothing, weapons, communication equipment, vision devices and provisions that suffice him for a long time. Technological progress has made this lightweight equipment easy to carry, for example: a smart helmet equipped with a computer that is used to integrate information from sensors and navigation equipment, as well as commands can be sent in writing to evade hearing difficulties caused by the noise of battle, and the soldier also carries a small identification device which can distinguish between enemy and a friend and can identify friendly fire. As for, logistics flow, it is mainly related to the shape of the theater of operations, the length of the logistics lines, weather conditions, the nature of the land, storage, maintenance and transportation systems.
We will review these systems to show their impact on the flow of logistics in modern warfare conditions.
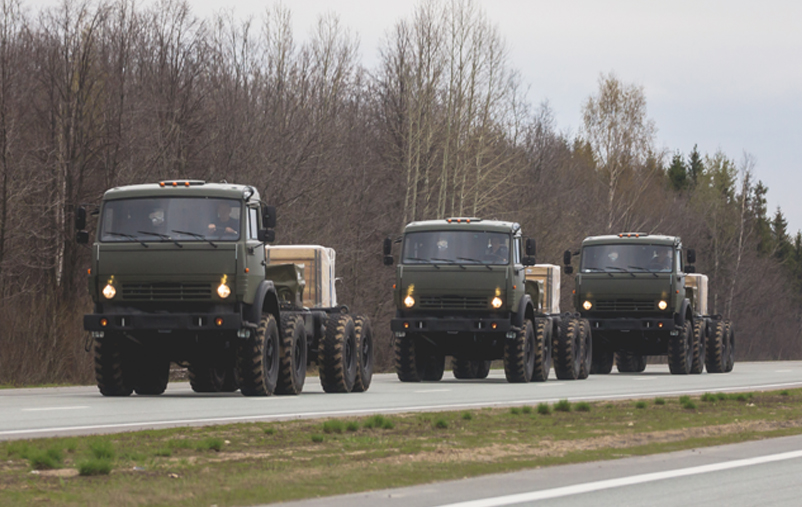
Transport System: The Gulf War revealed a number of important lessons that must be taken into account when planning modern wars, as it showed the inability of some countries to transport equipment and military forces to conflict areas due to their limited capabilities, while the United States of America was able to transport its forces within days, due to its ability to deploy forces, such as deployment of a large-scale air force in any region of the world within days, the deployment of a naval force within a week or two, and the deployment of the entire Vanguard Marine Corps, including its marine units, in a period ranging from two to four weeks. Therefore, it is necessary to reconsider the most appropriate method to move the logistics operations to long distances without exposing them to destruction by using all means of transportation as follows:
A. Road transportation:
Land transportation is represented in providing short, hidden and protected logistics and logistics lines at the state level and theater of operations, suitable for the passage of all types of vehicles and trucks, with the development of alternative roads used in emergency situations, and the introduction of appropriate modifications to the means of land transport, especially for large-sized equipment, while providing advanced unloading and transporting systems. New standard-spec trucks appeared, most notably: the French truck with a sliding tray. Countries are now moving to provide trucks equipped with self-loading cranes to overcome the problem of unavailability of means of loading and unloading in the front sites. Containers are transported directly from ships and transport planes to the stack zones, which saves time in the operations of loading, unloading and transportation, and countries are now moving towards achieving self-portable boxes or containers. That is, it was formed as one whole with the carrier vehicle, which is of different sizes to achieve the functions required in the cargo operations, and self-propelled forklifts appeared to transport and unload ammunition in the forward positions and in the artillery positions. Means of logistics also depended on determining their directions in the theaters of operations by using satellites’ links for easy access to the site without colliding with enemy sites.
B. Shipping:
Maritime transport in modern wars requires the preparation of an infrastructure of ports along the coasts of the country and they should be fully protected from land and air with the provision of alternative areas, as well as the provision of appropriate number of ships and cruisers and means of protecting them along the sea logistics lines with the provision of fast means of loading and unloading. There must be a close link between the military and civil authorities in the maritime transport operations. It is known that sea freight ships are very important for the transportation of large-sized equipment, ammunition, supplies, parts and spare parts to the fighting forces far from the motherland.
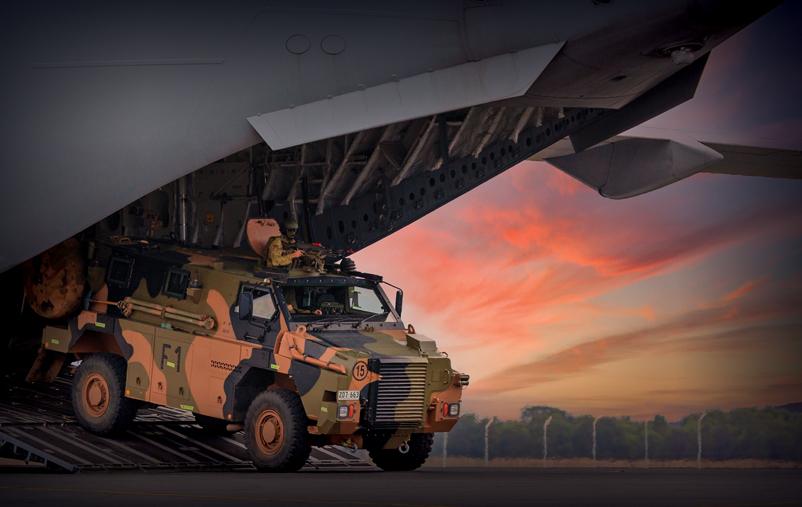
C. Air transport:
Air transport is considered one of the most important means of transportation in modern wars, because of its high speed in delivering all supplies at the right time and place, but this method is faced with difficulties in terms of landing runways that major countries are now working on developing their planes to land on short runways with loading huge quantities of materiel and equipment, case in point: the American plane (C5). Air transport is of particular logistical importance to supply isolated and besieged forces and in the absence of sufficient ground logistics lines. Parachuting and free-dropping, and helicopters have a major role in landing heavy equipment and transporting the wounded, and the importance of this emerged from the lessons learned from the Vietnam and Falklands wars.

Storage system: The logistics operations require modern and advanced storage systems to suit the continuing complexity in the field of weapons and equipment and the greater reliance in their operation on electronic processors, which require special specifications for storage areas with the provision of highly experienced personnel. Today, countries are moving to establish fortified areas throughout the country that help in rapid transfer of supplies to the expected theaters of operations.
But it is necessary to conduct a study to link the logistics of a large number of munitions to the type of weapon that will be fire them, the extent to which it will be exposed to malfunctions, and linking it to the spare parts required to repair this weapon. The elements of logistics must prepare estimates of the size of the stockpile of war materiel within the framework of limited budgets, which requires more accurate and more flexible calculations, so as to balance the real requirements of the forces of equipment, maintenance facilities, and spare parts with reducing military spending while preserving the combat capabilities of the forces.
Maintenance system: Diversity of weapons and means of transportation, their different standards and their continuous development, all of this will lead to new problems for the maintenance system, given that weapons and equipment will rely heavily on electro-optical systems and computers, which require highly- specialized maintenance operations personnel with high technical expertise for to deal with this development, and therefore maintenance systems need to be revised to adapt to the requirements of complex systems. Perhaps one of the most prominent solutions provided in this field is what is known as the integrated logistical support system for complex weapon systems, which starts from the design stage, and it is an administrative system that aims to ensure the support of the output over a lifetime, and this system includes logistical support analysis, which is a process of analyzing and identifying needs to support the output. Moreover, this process is not carried out only once, but is evaluated at limited intervals to ensure that the output is attributed to all stages of operation, and the development of the maintenance system based on information derived from practical operating experience. Undoubtedly, this will lead to reducing maintenance effort and saving costs, enabling the forces to obtain the best performance from their equipment, meeting maintenance requirements in different environments, and committing the armed forces to specific budgets.
Conclusion:
The Gulf War is unique in the logistics operations that were completed during it, and it may not be a measure of what may be needed in future conflicts, and it is not correct to take consumption rates and losses as an indicator for that purpose.
Modern or future war requires reconsidering the modern infrastructure of the state, because it is the pillars of achieving victory if it is linked to the requirements of the military campaign, such as developing airports and raising their efficiency, extending fuel pipelines and preparing the theater of operations with all its needs in terms of engineering, transportation, maintenance and other economic aspects. The logistics operations in modern war will depend entirely on the capabilities of the state, and if the twentieth century has been called the “information century and the nuclear century” in which many military concepts and strategies have changed, and in the latter half of it, technology has been harnessed to serve the armies and their goals. It saved a lot of effort and time.
If this is the case of the twentieth century, what will be the state of the twenty-first century? It is the century of “satellites”. In this century, there is no doubt that many strategies and concepts will change. There may be a change in the principles of war itself and the principles of logistics, because the means by which the battles of this century will be conducted will inevitably change. Satellites entered as a key player in deciding the outcome of battles.
The plans of the future armies were based on how to make full use of this advanced means. The features of these changes have begun to appear in some advanced armies. At the level of support, some armies have raised the efficiency of organizational support in maintenance and requalified it to replace direct support, so that the vehicles are maintained and the momentum of the battle is maintained. The vehicle itself has been requalified to require automatic support via satellites, and without the intervention of the driver, it monitors the consumption levels of fuel and ammunition, and sends direct reports to the higher levels, where the support reaches it in a timely manner.
At the level of transportation, the countries that deploy their forces outside their countries are primarily interested in reaching the theater of operations in a timely manner, and since this can only be done by air transport, the US Army has applied the experience of its “STYKER BRIGADE” in which combat vehicles sizes have been reduced to a level where they can transport as many vehicles as possible into the theater of operations. These vehicles are technically equipped so that they can perform better tasks albeit of their smaller size. Based on these fundamental modifications, the airlift can transport an equipped brigade to the theater in 96 hours, a division in 120 hours, and a corps in 30 days.
One of the features of logistics in the new century is effective communication and cooperation between the military sector and the private sector. Many military institutions have been keen to create a direct and strong connection between their sectors and private sector institutions, in the field of education and training, and the beneficiary of this communication is undoubtedly the military institutions. Because private sector companies and institutions, by virtue of their profitable goals and trends, are keen to acquire the latest in modern technology, to improve their production and performance, unlike military institutions which receive these technologies late.
Before concluding, we cannot fail to mention that the science of logistics has become an academic science, and many Western universities are currently granting degrees in the sciences of logistics, such as masters and doctorates. The science of logistics is a science that has a direct link with other academic sciences, such as economics, statistics, and management. The evidence proves that the armies that excelled in their battles and proved their worth are the ones that assigned the management of logistics to commanders with high scientific and planning competencies, while we see the opposite in the less advanced armies! .
» By: Dr. Moeen Ahmed Mahmoud
(A Military researcher and strategist)